Table of Contents
Difference between DNA and Genes
Organic molecules like RNA and DNA are essential for the growth and reproduction in living organisms. Out of the two nucleic acids, DNA contributes directly to cell division and the transfer of information in the form of genes. DNA is a double-helix structure, whereas genes are located on chromosomes. These are responsible for carrying hereditary material from parents to off-springs. DNA and Genes are the structures that cannot be seen with the naked eye, but are observed under complex microscopes. You can observe their detailed structure better in electron microscopes.
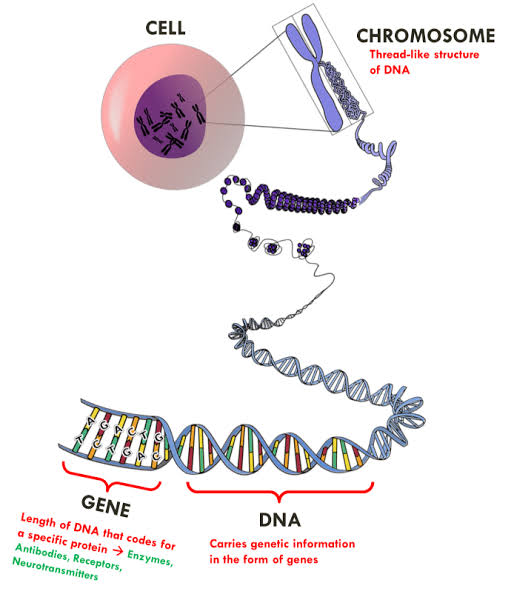
Despite their role in carrying hereditary information, DNA and genes differ in structure, and exact functions. This article explains both of them in detail and highlights the key differences between DNA and genes.
Comparison Table
| Characteristics | DNA | Gene |
| Structure | Double-helical | Ribbon divided into segments |
| Composition | Nucleotides, a ribose sugar, and phosphate group | RNA or DNA |
| Function | Information regarding the survival, development, and reproduction | Information of characteristics possessed by an organism |
| Location | Nucleus | Chromosomes |
| Packing | Tight | Loose |
| Pairing | A with T and C with G | Varying ACGT combinations |
| MicroRNA | Non-coding DNA not transcribed | Transcribed |
| Repetitiveness | More | Less |
What is DNA?
DNA or Deoxyribonucleic acid is an important organic compound in living organisms that stores and expresses genetic information. Sometimes, the birthmarks you see on your body are the results of genetic changes or alterations in DNA. It was first discovered by Johannes Friedrich Miescher, a Swiss biologist, in the year 1869. DNA is responsible for passing the characteristics from generation to generation in all organisms, including bacteria and viruses.
Let’s have a look at the structure of DNA.
DNA Structure
DNA is a double helix structure, specified for special functioning. It is made up of two long and thin twisted strands which hold the blueprint. The building blocks of DNA are nucleotides comprising nitrogen bases, pentose sugar, and a phosphate group. The nitrogen bases could be purines or pyrimidines, depending on their composition. Purines comprise adenine and guanine, while cytosine and thymine are pyrimidine bases. Each strand of the helical DNA contains a complementary nitrogen base.
The structure of DNA looks like a ladder twisted at both ends. It is responsible for carrying the genetic information, mutations, and replication processes in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. During cell division, equal division of DNA is critical for the growth and development of new cells.
A DNA molecule has four types of bases:
- Adenine
- Thymine
- Guanine
- Cytosine
The formation of DNA results from specific combinations of nucleotide bases. Cytosine always binds to Guanine and Adenine pairs with thymine.
Function of DNA
DNA contains all the information needed for synthesizing proteins and the characteristics an organism acquires. The DNA sequence is decoded into RNA, which further translates into proteins. Each DNA sequence accounts for a specific protein and the organism’s genotypic or phenotypic characteristics.
What are Genes?
According to the source, there are numerous chromosomes in a body that contain hereditary informational units called genes. There are about thirty thousand genes in the human body in every cell. They account for different characteristics unique to organisms decided through inherited genes. Thus, genes determine the features in the body.
Genes Structure
Genes in most organisms are made up of DNA, except viruses, which may have RNA as the genetic structure. Eventually, DNA-comprising genes have the same nucleotides – Adenine (A), Cytosine (C), Guanine (G), and Thymine (T). However, different nucleotide pairings may give rise to particular characteristics in different people.
Function of Genes
The human body has 23 pairs of chromosomes with genes accounting for different functions. The chromosomes pass this genetic information from the parents to daughter cells. Some genes carry information to make different types of proteins; however, not all genes possess this data. The primary function of genes is to decide almost everything in the human body. They decide all traits possessed by an individual. However, human activities like smoking can alter gene functioning.
Differences between DNA and Genes
Definition
DNA
DNA is defined as a molecule that carries genetic information for the development and functioning of the body.
Genes
Genes are DNA stretches present on chromosomes that determine the different characteristics of an organism.
Structure
DNA
DNA comprises a double-helical structure with nucleotides on both bonded to each other through hydrogen bonds.
Gene
While the exact structure of a gene is poorly understood, the drawing of a gene looks like a ribbon divided into segments.
Composition
DNA
DNA is composed of nucleotides, ribose sugar, and a phosphate group.
Genes
At the same time, genes are made up of DNA or sometimes RNA.
Function
DNA
DNA contains all the information regarding survival, development, and reproduction.
Genes
Genes account for the characteristics possessed by an organism.
Location
DNA
DNA is found in the nucleus of the cell that is readily observed under electron microscopes, like scanning tunneling microscopes.
Genes
On the other hand, genes reside on chromosomes.
Packing
DNA
DNA is tightly packed to fit in the nucleus in free form.
Genes
In comparison, genes are loosely packed DNA segments on chromosomes.
Nucleotide Pairing
DNA
Adenine pairs with thymine, and guanine pairs with cytosine in DNA.
Genes
Whereas genes comprise different combinations of ACGT for unique characteristics.
MicroRNA
DNA
Non-coding DNA cannot be transcribed into RNA for protein synthesis.
Genes
Genes containing information for protein synthesis may transcribe into RNA.
Repetitiveness
DNA
Genomic DNA is often highly repetitive, with around two-thirds of the sequence comprising repetitive elements.
Genes
However, genes are less repetitive compared to DNA segments.
The Bottom Line
DNA and Genes play an essential role in the growth and reproduction of living organisms. They contain genetic information about an organism’s characteristics. DNA in eukaryotes and prokaryotes carries information from the parent cells to the daughter cells. On the other hand, genes reside in chromosomes formed by euchromatin and heterochromatin. Both of them comprise purine and pyrimidine nucleotide bases. DNA contains a particular sequence of nucleotides, whereas genes may have varying combinations to give particular characteristics to organisms.
Hopefully you enjoyed this amazing article. Keep visiting Daily Human Care for more interesting health articles.



